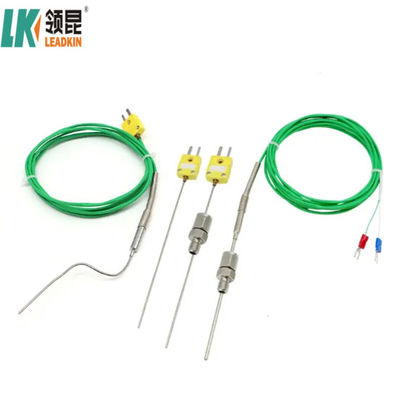
Type for Sheath Wire Type K:
| Product Name |
Code |
Type |
Shaeth Material |
Outside Dia. |
Temperature |
| NiCr-NiSi /NiCr-NiAl |
KK |
K |
SS304 SS316 |
0.5-1.0 |
400 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
600 |
| 4.0-8.0 |
800 |
| SS310 Inconel600 |
0.5-1.0 |
500 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
800 |
| 4.0-6.4 |
900 |
| 8.0-12.7 |
1000 |
| NiCrSi-NiSi |
NK |
N |
SS304 SS316 |
0.5-1.0 |
400 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
600 |
| 4.0-8.0 |
800 |
| SS310 Inconel600 |
0.5-1.0 |
500 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
800 |
| 4.0-6.4 |
900 |
| 8.0-12.7 |
1000 |
| NiCr-Konstantan |
EK |
E |
SS304 SS316 |
0.5-1.0 |
400 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
600 |
| 4.0-8.0 |
800 |
| Fe-Konstantan |
JK |
J |
SS304 SS316 |
0.5-1.0 |
400 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
600 |
| 4.0-8.0 |
800 |
| Cu-Konstantan |
TK |
T |
SS304 SS316 |
0.5-1.0 |
400 |
| 1.5-3.2 |
600 |
| 4.0-8.0 |
800 |
| RhPt10-Ph |
SK |
S |
Inconel600 |
6.0-12.7 |
1100 |
Different temperature measuring media and service conditions have an impact on the service life and temperature range of armored thermocouples, the data in the table is only recommended data.
Accuracy for Sheath Wire Type K
| Type |
Class I |
Class II |
| Accuracy |
Temp.Range |
Accuracy |
Temp.Range |
| K |
±1.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
±2.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
| ±0.4% |
375℃-1000℃ |
±0.75% |
375℃-1000℃ |
| N |
±1.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
±2.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
| ±0.4% |
375℃-1000℃ |
±0.75% |
375℃-1000℃ |
| E |
±1.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
±2.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
| ±0.4% |
375℃-800℃ |
±0.75% |
375℃-800℃ |
| J |
±1.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
±2.5℃ |
-40~375℃ |
| ±0.4% |
375℃-800℃ |
±0.75% |
375℃-800℃ |
| T |
±0.5℃ |
-40~125℃ |
±1.0℃ |
-40~125℃ |
| ±0.4% |
125℃-350℃ |
±0.75% |
125℃-350℃ |
| S |
0-1100℃ |
±1.0℃ |
0-1100℃ |
±1.5℃ |
Product Description:
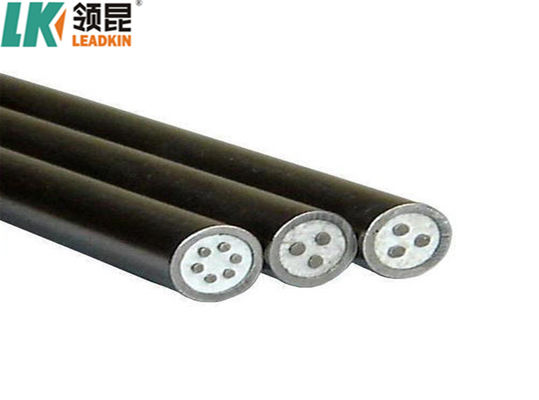
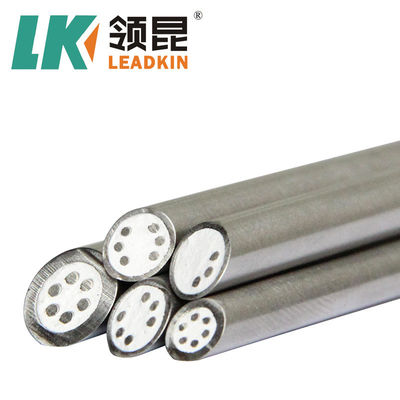
Sheath cable, also known as sheathed cable or armored cable, refers to a type of electrical cable that is encased in a protective outer layer or sheath. This sheath can be made from various materials and serves multiple purposes, including physical protection, insulation, and environmental resistance. Sheath cables are commonly used in a variety of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial installations.
Key Features of Sheath Cables:
Protection:
The sheath provides mechanical protection against impacts, abrasion, and environmental factors. This is especially important in industrial or outdoor settings where cables may be exposed to harsh conditions.
Material:
The sheath can be made from a variety of materials, including:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Common for general-purpose cables due to its flexibility and resistance to moisture.
XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): Offers higher thermal resistance and is used in applications requiring better insulation properties.
Rubber: Provides excellent flexibility and weather resistance, making it suitable for outdoor or heavy-duty applications.
Metal: In armored cables, a metallic sheath (typically steel or aluminum) is used for additional protection against physical damage.
Characteristics:
Temperature Range: MI cables can operate in extreme temperature environments, often up to 1200°C.
Durability: The metal sheath provides durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
Flexibility: Despite their rugged construction, MI cables can be made flexible for installation in various applications.
Applications:
Used with thermocouples in high-temperature and hazardous environments (e.g., power plants, petrochemical industries).
Suitable for temperature measurement in nuclear applications, furnace monitoring, and cryogenic environments.
Commonly found in applications where electrical and thermal insulation is critical.
Advantages:
High thermal conductivity and rapid response times.
Excellent protection against mechanical damage and chemical exposure.
Long lifespan, even under extreme conditions.
Disadvantages:
Typically more expensive than standard thermocouple leads.
Installation can be more complicated due to stiffness and weight.
Conclusion:
Both thermocouples and mineral insulated cables play critical roles in temperature measurement and control in various industries. Understanding their characteristics, advantages, and limitations helps in selecting the right components for specific applications. Whether you need reliable temperature readings in a furnace or require durable cables for harsh environments, these technologies are essential in modern industrial processes.
Applications :
RTD and Thermocouple Sensors Constructed Using MI Cable are Used Extensively in Various Applications such as:.
- Solid waste incinerators.
- Sintering powdered metals.
- Firing ceramic materials.
- Gas or oil fired furnaces.
- Fuel fired heat exchangers.
- Box furnaces.
- Nuclear or hydrocarbon based energy plant.
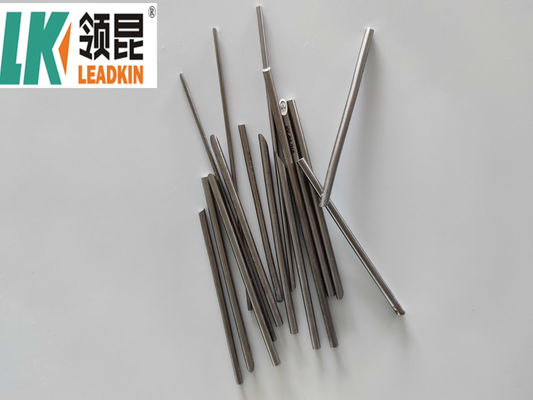
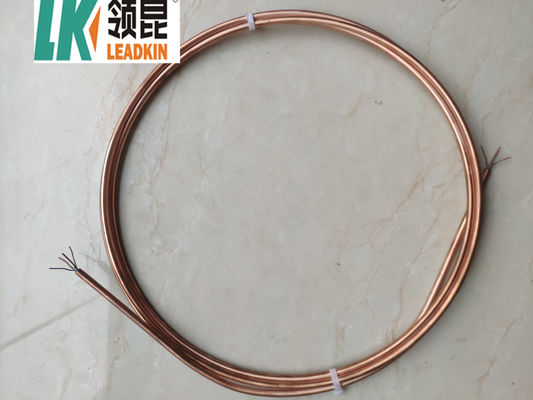
Product Pictures:

Company Information:
A. Main Products


B. Package
We add heat shrink tubing and plastic film to make sure high insulated resistance.
Except marking notes, we also have pass card and test report for every coil cable.

C. Mi cable Production line
We have high - quality professional products, as well as advanced product lines and equipments. All of the products comply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world.Along the increasing market demands, we continuously satisfy customers by updating products to improve prouduction systems, improve quality.

Order Notice:
1. Accurate quotation.
2. Confirm the price, trade term, lead time, payment term etc.
3. LEADKIN sales send the Proforma Invoice with LEADKIN seal.
4. Customer arranges the payment for deposit and sends us bank slip.
5. Middle Production-send photos to show the production line which you can see your products in . Confirm the estimated delivery time again.
6. End Production-Mass production products photos.
7. Clients make payment for balance and LEADKIN ships the goods. Inform the tracking number and check the status for clients.
8. The order is finished perfectly when you receive the goods and get satisfied with them .
9. Feedback to LEADKIN about Quality , Service, Market Feedback & Suggestion. And we will do better .
FAQ:
1. What is a thermocouple?
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor that consists of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end. When the junction experiences a change in temperature, it generates a voltage that can be correlated to temperature changes.
2. How does a thermocouple work?
Thermocouples operate on the principle of the Seebeck effect, which states that a voltage is produced when two different metals are joined and there is a temperature difference between the junctions. This voltage can be measured and interpreted to provide a temperature reading.
3. What are the types of thermocouples?
Common types of thermocouples include:
Type K (Chromel-Alumel): General-purpose, wide temperature range.
Type J (Iron-Constantan): Good for lower temperature ranges.
Type T (Copper-Constantan): Ideal for cryogenic applications.
Type E (Chromel-Constantan): Good sensitivity, suitable for low temperatures.
Type N (Nicrosil-Nisil): Stable at high temperatures and resistant to oxidation.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 












